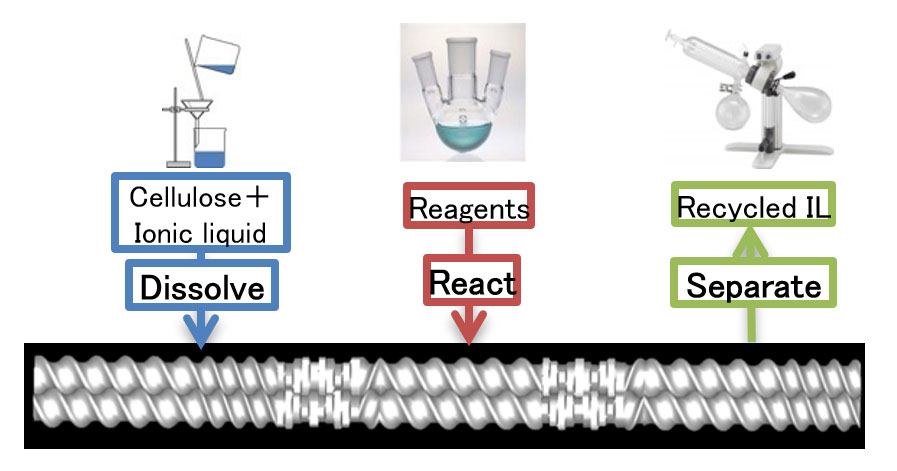
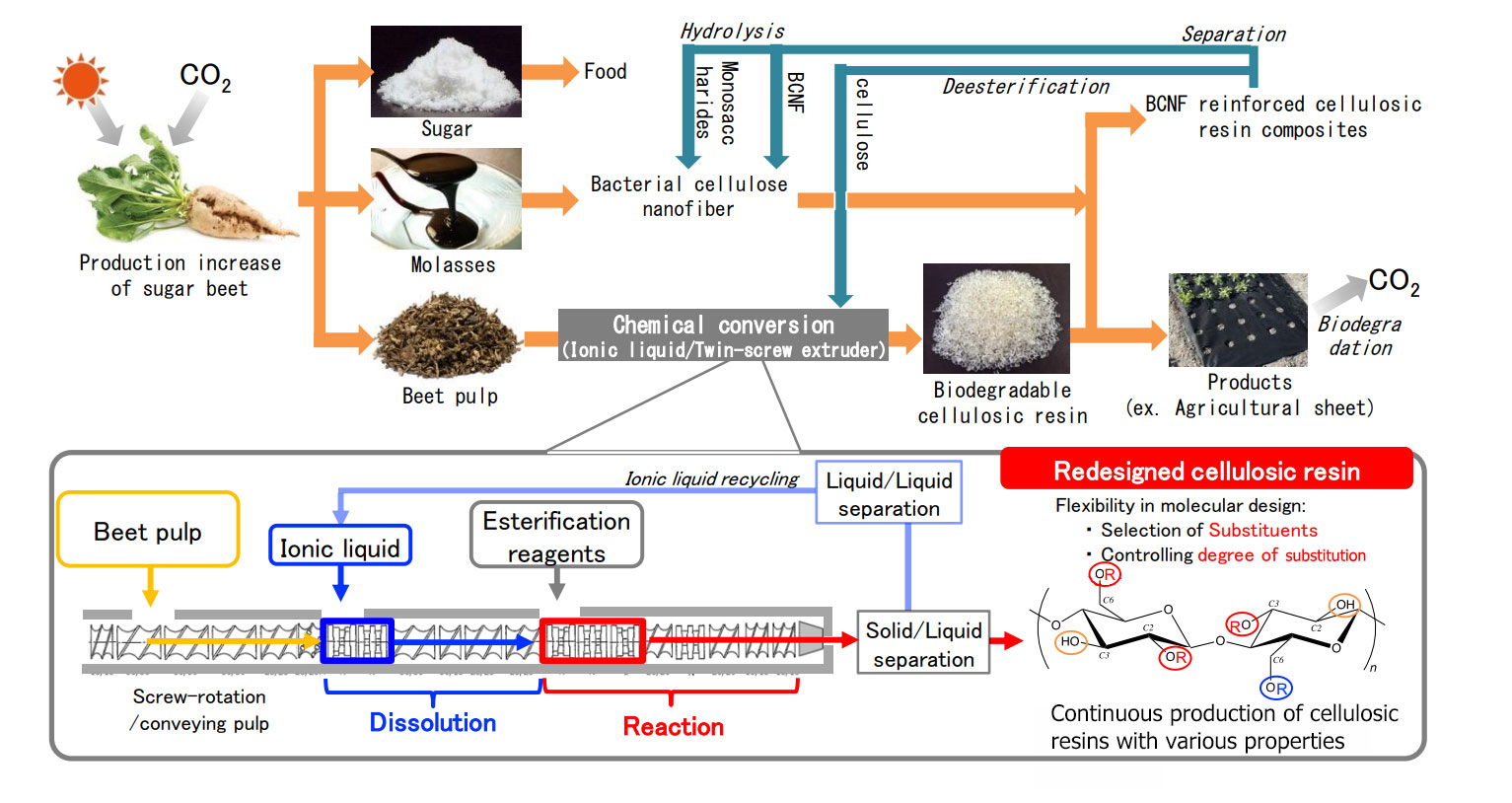
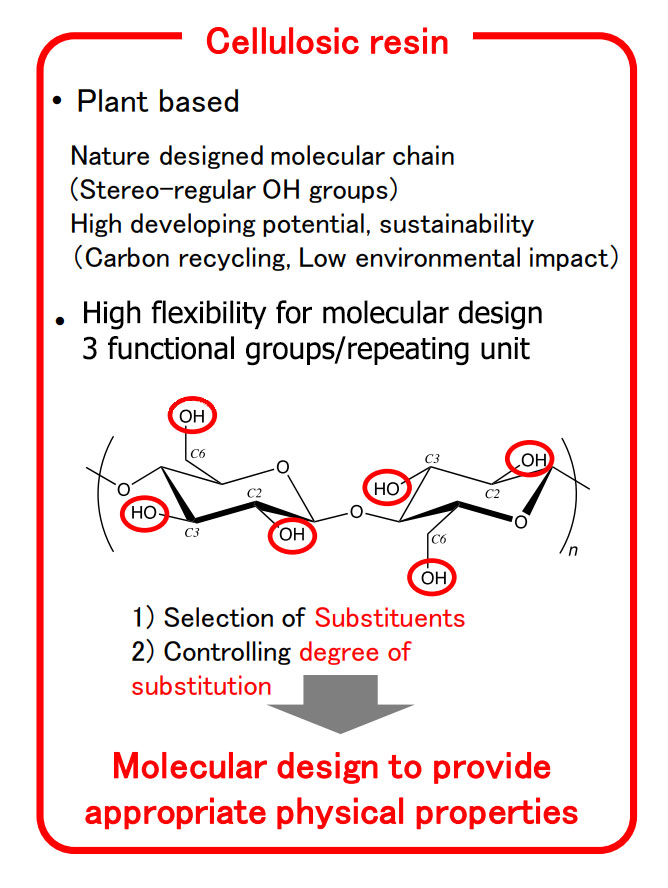
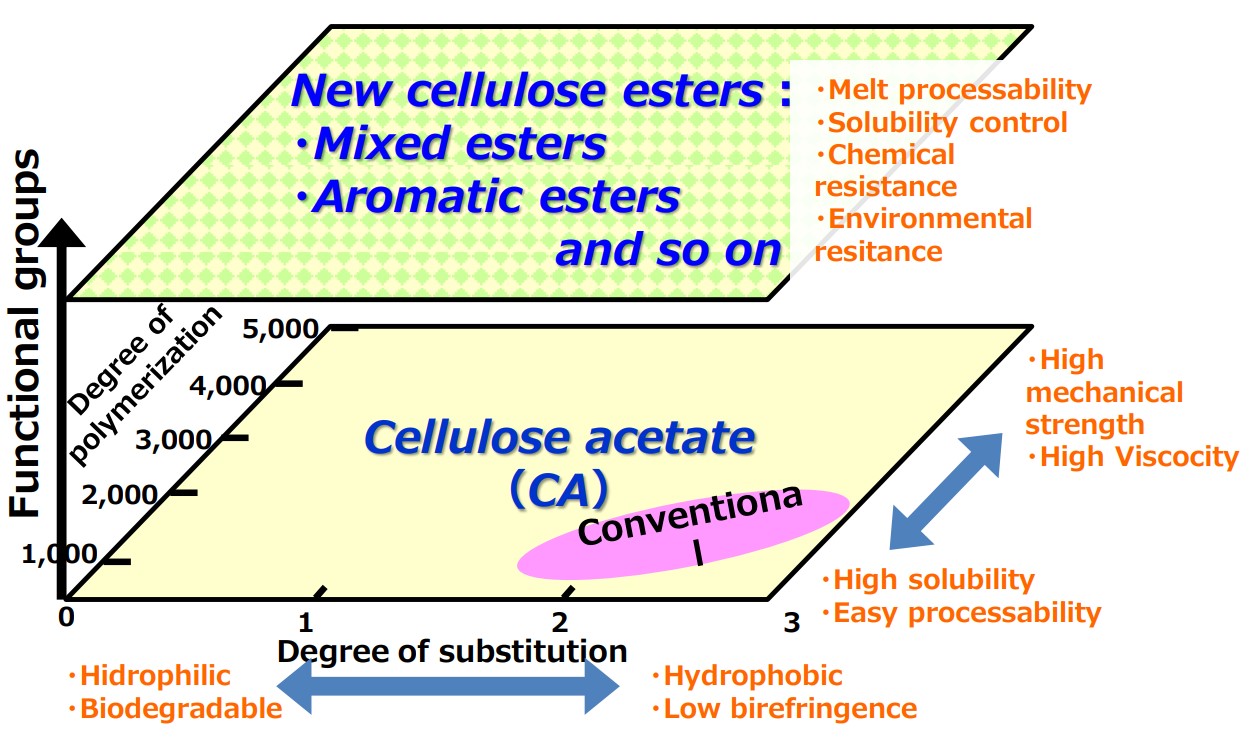
Agricultural cellulose esters
Agricultural cellulose esters
Redesigning cellulosic resin
High flexibility for designing cellulosic resins
Advantages over existing bioplastics
|
|
Biopolyethylene (bioPE) |
Polylactide(PLA) |
Starch resin |
Conventional cellulose acetate (CA) |
Redesigned cellulosic resin |
|
Raw material |
Sugarcane |
ex. Corn |
ex. Corn |
Wood pulp |
Agricultural waste |
|
Designability |
None |
None |
Moderate |
Low |
High |
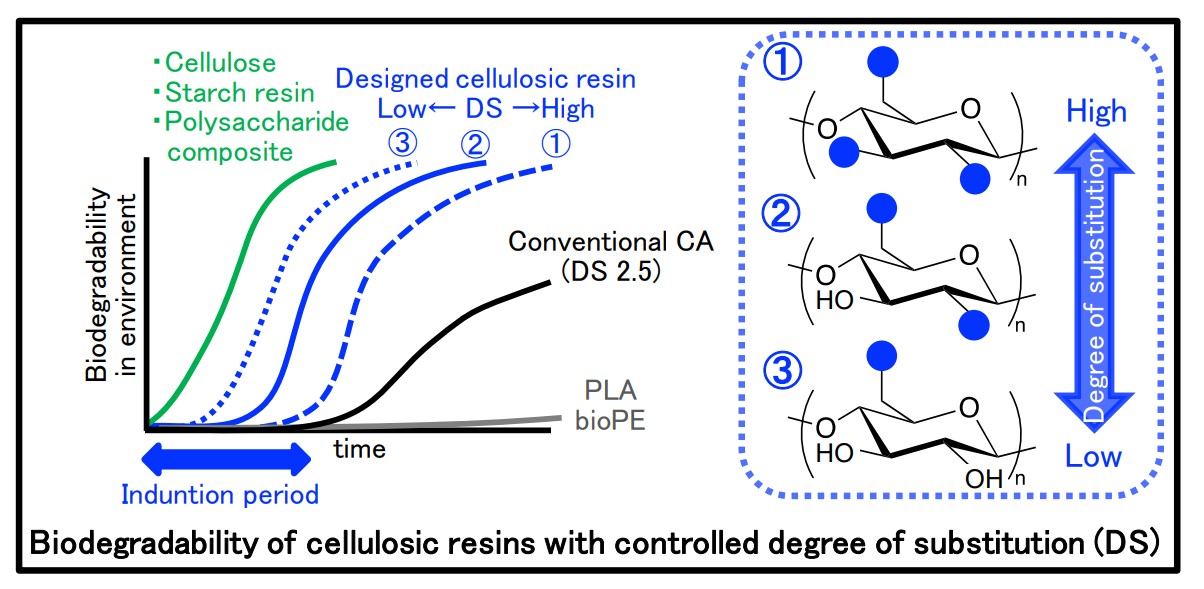
Biodegradability of cellulosic resin
Advantages over existing bioplastics
|
|
Biopolyethylene (bioPE) |
Polylactide (PLA) |
Starch resin |
Conventional cellulose acetate (CA) |
Redesigned cellulosic resin |
|
in Soil |
none |
only in Composting |
moderate |
Long induction period |
Controllable induction period |
|
in Ocean |
none |
none |
moderate |
Long induction period |
Controllable induction period |
Biodegradability of cellulosic resins with controlled degree of substitution (DS)
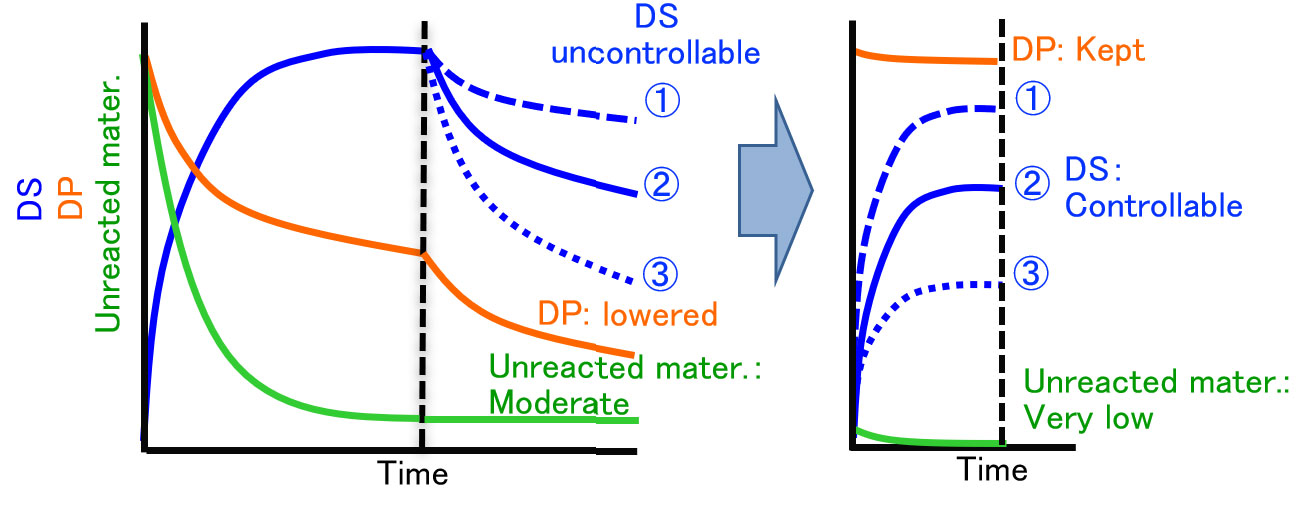
Productivity of Cellulosic Resins -Innovations in Ionic Liquid (IL)/Reacive Extrusion (REX) Method-
Advantages of IL/REX method over conventional methods for producing cellulosic resins
|
|
Conventional method |
IL/REX method |
|
Production step |
Multi steps |
One step |
|
Production time |
48 hours |
within 10 min |
|
Substitution |
Only One at same time |
Multi at same time |
|
DS control |
Uncontrollable |
Arbitrarily controllable |
|
Flow synthesis |
Impossible |
Possible |
|
Unreacted raw material |
Moderate |
Very low |
|
Decrease of degree of polymerization (DP) |
High |
Very low |
| Conventional |
IL method |
|
|
Esterification |
Deesterification |
Esterification |
- Continuous production in a short time
Energy saving, High productivity - Low material loss
High efficiency, low environmental impact - General machine
Easy to be popular